The original intersection of demand and supply occurs at e 0 if demand shifts from d 0 to d 1 the new equilibrium would be at e 1 unless a price ceiling prevents the price from rising.
Price floor and ceiling analysis.
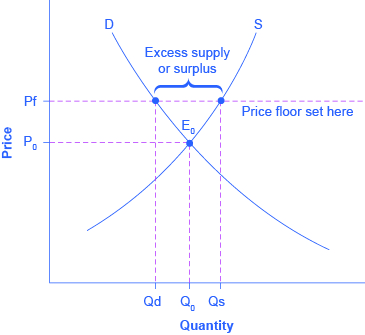
A price floor is an established lower boundary on the price of a commodity in the market.
If the price floor is low enough below the equilibrium price there are no effects because the same forces that tend to induce a price equal to the equilibrium price continue to operate.
But this is a control or limit on how low a price can be charged for any commodity.
A government law that makes it illegal to charger lower than the specified price.
Efficiency and price floors and ceilings.
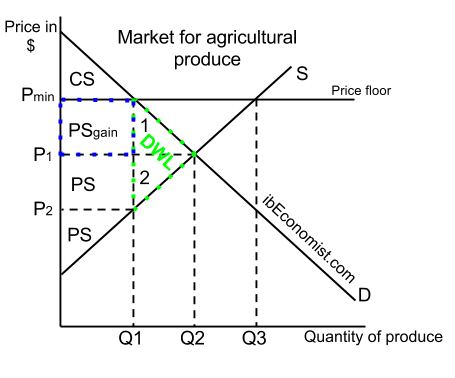
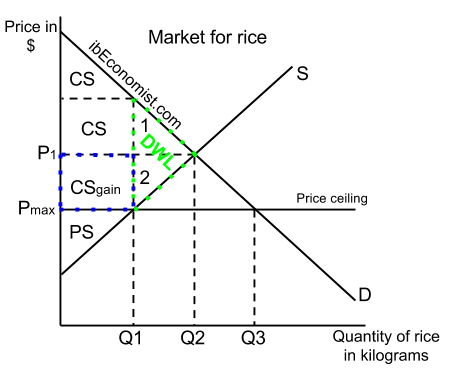
Price floors and ceilings are inherently inefficient and lead to sub optimal consumer and producer surpluses but.
The original consumer surplus is g h j and producer surplus is i k.
Example breaking down tax incidence.
Percentage tax on hamburgers.
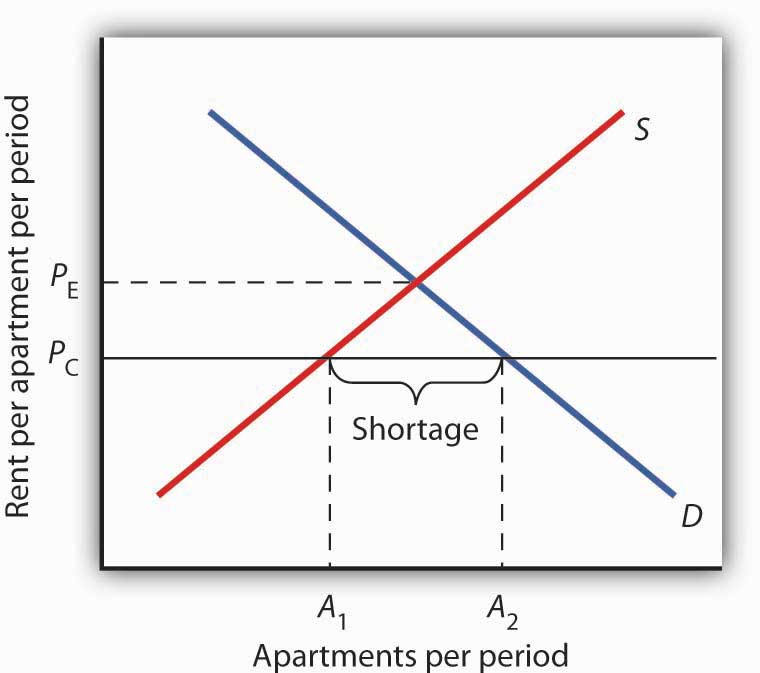
If the price is not permitted to rise the quantity supplied remains at 15 000.
Governments usually set up a price floor in order to ensure that the market price of a commodity does not fall below a level that would threaten the financial existence of producers of the commodity.
Two things can happen when a price floor is implemented.
The theory of price floors and ceilings is readily articulated with simple supply and demand analysis.
In this case there is no effect on anything and the equilibrium price and quantity stay the same.
The current equilibrium is 8 per movie ticket with 1 800 people attending movies.
This is usually done to protect buyers and suppliers or manage scarce resources during difficult economic times.
Once you learn the basics of support and resistance it is possible to guess whether the stock is.
The price ceiling is below the equilibrium price.
Taxes and perfectly inelastic demand.
Price floors equilibrium price floor d quantity of icecreams price 3 2 200 4 s 100 d quantity of icecreams price 3 2 200 600 4 s 100 surplus price ceiling price controls.
Finding the floor and ceiling of a stock involves learning technical analysis of stock charts.
Consider a price floor a minimum legal price.
Figure 2 b shows a price floor example using a string of struggling movie theaters all in the same city.
This is the currently selected item.
The effect of government interventions on surplus.
Price floors and price ceilings are government imposed minimums and maximums on the price of certain goods or services.
Price floors why a price floor causes inefficiency inefficient allocation of sales among sellers price floors lead to inefficient allocation of sales among.
It is legal minimum price set by the government on particular goods and services in order to prevent producers from being paid very less price.
Price ceilings and price floors.
Taxation and dead weight loss.