Perhaps the best known example of a price floor is the minimum wage which is based on the normative view that someone working full time ought to be able to afford a basic standard of living.
Price floor graphically.
A price floor is a minimum price enforced in a market by a government or self imposed by a group.
A few crazy things start to happen when a price floor is set.
Perhaps the best known example of a price floor is the minimum wage which is based on the normative view that someone working full time ought to be able to afford a basic standard of living.
We are going to pass a minimum wage.
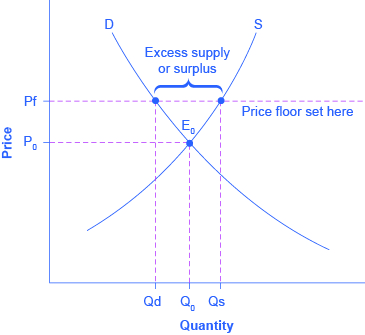
In the first graph at right the dashed green line represents a price floor set below the free market price.
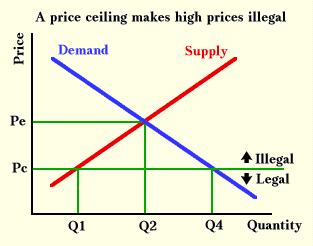
A price ceiling is the legal maximum price for a good or service while a price floor is the legal minimum price.
Price ceilings can also be set above equilibrium as a preventative measure in case prices are expected to increase dramatically.
You ll notice that the price floor is above the equilibrium price which is 2 00 in this example.
More specifically it is defined as an intervention to raise market prices if the government feels the price is too low.
This is a minimum price in the market.
This graph shows a price floor at 3 00.
In this case since the new price is higher the producers benefit.
In this case the floor has no practical effect.
The graph below illustrates how price floors work.
A price floor or a minimum price is a regulatory tool used by the government.
It is legal minimum price set by the government on particular goods and services in order to prevent producers from being paid very less price.
It has to be at least 7 an hour so this right over here is a price floor.
We are going to pass a law minimum wage that says any employer has to pay at least 7 an hour 7 an hour.
A price floor is the lowest legal price that can be paid in markets for goods and services labor or financial capital.
Typical examples include minimum wage agricultural support price and price agreed by an oligopoly.
Like price ceiling price floor is also a measure of price control imposed by the government.
National and local governments sometimes implement price controls legal minimum or maximum prices for specific goods or services to attempt managing the economy by direct intervention price controls can be price ceilings or price floors.
When we talked about rent control that was a price ceiling.
It tends to create a market surplus.
Drawing a price floor is simple.
A price floor could be set below the free market equilibrium price.
When a price ceiling is put in place the price of a good will likely be set below equilibrium.
For a price floor to be effective the minimum price has to be higher than the equilibrium price.
A price floor is the lowest legal price that can be paid in a market for goods and services labor or financial capital.